Researchers Get $10,000 for Hacking Google Server with Malicious XML
A critical vulnerability has been uncovered in Google that could allow an attacker to access the internal files of Google’s production servers. Sounds ridiculous but has been proven by the security researchers from Detectify.
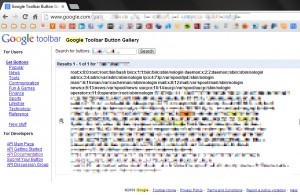
 The team of researchers found a loophole after they noticed that Google Toolbar Button Gallery allows users to customize their toolbars with new buttons. So, for the developers, it is easy to create their own buttons by uploading XML files containing metadata for styling and other such properties.
The team of researchers found a loophole after they noticed that Google Toolbar Button Gallery allows users to customize their toolbars with new buttons. So, for the developers, it is easy to create their own buttons by uploading XML files containing metadata for styling and other such properties.
This feature of Google search engine is vulnerable to XML External Entity (XXE). It is an XML injection that allows an attacker to force a badly configured XML parser to "include" or "load" unwanted functionality that can compromise the security of a web application.
“The root cause of XXE vulnerabilities is naive XML parsers that blindly interpret the DTD of the user supplied XML documents. By doing so, you risk having your parser doing a bunch of nasty things. Some issues include: local file access, SSRF and remote file includes, Denial of Service and possible remote code execution. If you want to know how to patch these issues, check out the OWASP page on how to secure XML parsers in various languages and platforms," the researchers wrote on a blog post.
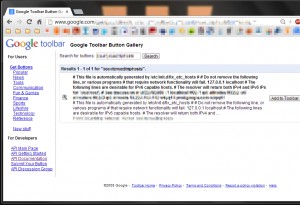
Using the same, the researchers crafted their own button containing fishy XML entities. By sending it, they gain access to internal files stored in one of Google's production servers and managed to read the “/etc/passwd” and the “/etc/hosts” files from the server.
By exploiting the same vulnerability the researchers said they could have access any other file on their server, or could have gain access to their internal systems through the SSRF exploitation.
The researchers straight away reported the vulnerability to the Google’s security team and rewarded with $10,000 (€7,200) bounty for identifying an XML External Entity (XXE) vulnerability in one of the search engine’s features.
Axarhöfði 14,
110 Reykjavik, Iceland