Crooks used SQL injections to hack Drupal sites and install fake ransomware
The first victims recorded complaining about this new strain of ransomware appeared in late March, on the official Drupal forums.
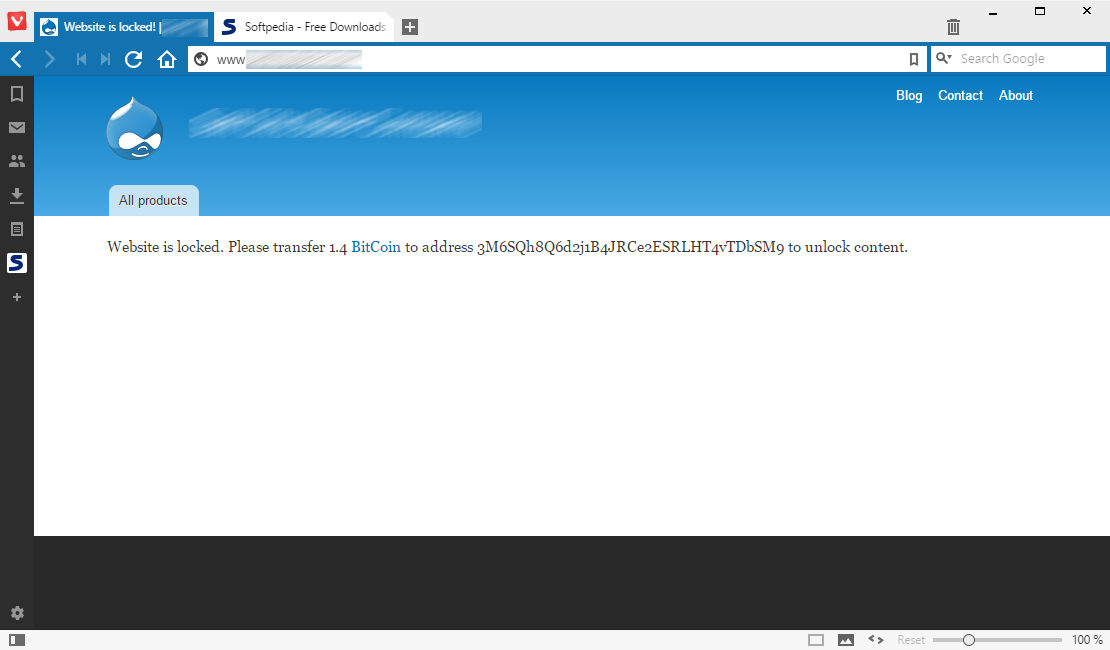
 Site admins were describing their websites as "being locked" with a message that read: “Website is locked. Please transfer 1.4 BitCoin to address 3M6SQh8Q6d2j1B4JRCe2ESRLHT4vTDbSM9 to unlock content.”
Site admins were describing their websites as "being locked" with a message that read: “Website is locked. Please transfer 1.4 BitCoin to address 3M6SQh8Q6d2j1B4JRCe2ESRLHT4vTDbSM9 to unlock content.”
A quick Google search for the Bitcoin address reveals that most websites are running on the Drupal CMS platform. Information provided by Stu Gorton, CEO and Co-Founder of Forkbombus Labs, shows that the first infections started appearing on March 11 but really picked up speed after March 18. Forkbombus Labs says that the threat actor behind this campaign starts by scanning websites for the presence of /CHANGELOG.txt (Drupal CMS specific file) and /joomla.xml files.
The attacker's scanning bot extracts the Drupal site's version, then uses the CVE-2014-3704 vulnerability to break into the affected websites and eventually change the admin user's password. CVE-2014-3704 is an SQL injection vulnerability that affects Drupal 7.x installations prior to version 7.32. Even if the bot scans for the joomla.xml file, there are no reports of infected Joomla sites, and Mr. Gorton told the threat actor removed Joomla scanning at a later stage.
"Ransomware is actually "fauxsomeware""
Mr. Gorton also informed that once the threat actor gains control of the site with the help of the SQL injection, automated operations set up a new page on the Drupal site that contains a file upload form. The crook's bot then uses this form to upload various scripts that extract emails from the Drupal database and make them available in "/sites/default/files/" as downloadable files. The .htaccess in this folder is also deleted, so the attacker can access the page and download the files.
After this ends, the last uploaded file is a binary file written in the Go programming language, which is the actual ransomware. This Go binary deletes the file upload form and replaces it with the ransom note seen above.
"It should be clear that this is fauxsomeware, rather than ransomware, as nothing is encrypted or truly locked," Mr. Gorton told. "Simply, the content of the available nodes are replaced with the new message. It appears however the bot has trouble replacing the information on nodes with atypical formats, as several compromises we've witnessed still have a large portion of their data intact."
Mr. Gorton also noted the existence of a C&C server infrastructure behind these attacks on Drupal sites, but the company is still investigating its mode of operation.
"Around 400 sites were infected, nobody paid the ransom"
Approximately 400 websites seem to be infected with this ransomware at the time of writing. The Bitcoin address used for the ransom has no transactions recorded, meaning nobody has paid the ransom as of this time.
The same thing happened earlier this year with CTB-Locker and KimcilWare, two ransomware variants also targeting websites. Even if these two threats encrypted the site's files, admins never paid the ransom because even the worst Web hosting service provides automatic backups from where they could retrieve a clean version of their site.
As for this Drupal-targeting ransomware, this looks to be another attempt at developing ransomware for the Web that has failed as miserably as CTB-Locker and KimcilWare. And to be fair, just by looking through the few Drupal sites hit by this ransomware, they all seem to have been abandoned by their creators, so no real harm has been done. If you remember installing a Drupal CMS lately, make sure to either upgrade it or delete it if it has no purpose or just an older test site.
Axarhöfði 14,
110 Reykjavik, Iceland














